Impulse Force Presentation during Ball Kicking by Lower Limb Exoskeleton with MR Fluid Brake
ID:11
Submission ID:57 View Protection:ATTENDEE
Updated Time:2023-03-14 09:11:11 Hits:878
Poster Presentation
Abstract
Introduction
Recently, the widespread use of HMD has made it easier to access virtual reality (VR) spaces. This has led to the development of force-feedback devices that give the user the sensation of manipulating a virtual object. Typical installation-type devices are large and limit the range of movement of the user. Therefore, the authors [1] have developed an exoskeleton-type force feedback device for the lower limbs using MR fluid brakes to present the sensation of walking and falling. The objective of this study is to present an impulsive force to the lower limb using MR fluid brakes.
Design
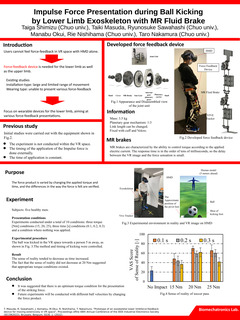
Figure 1 shows the proposed force feedback device. The driving axes are located at the hip and knee joints. The drive shafts are composed of a MR fluid brake, a reduction gear, and an encoder. The device is secured to the body with a cuff and Velcro tape.
Experiment
The purpose of this experiment is to verify the difference in the perception of the force when the force product generated by the braking torque of the MR fluid brake is changed for the presentation of the force. The experimental action was assumed to be a kick in a soccer pass, and the conditions under that an electric current was applied to each joint at the moment of kicking the ball in the virtual space are varied.
Figure 2 shows the results of the experiment. Compared to the condition in which no force was applied, the VAS (Visual Analog Scale) score of the sense of reality was improved in the condition in which a force was applied. At the maximum, a torque of 20 Nm and a duration of 0.1 s gave a sense of reality of about 70%. These results suggest that there is an optimum torque condition for the presentation of the striking force by MR braking.
References
[1] T. Masuda, R. Sawahashi, J. Komatsu, M. Okui, R. Nishihama, T. Nakamura, "Prototype of an exoskeletal lower limb force-feedback device for moving extensively in VR space", Proceedings of the 48th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON2022), Brussels, Belgium, SS30_1, (2022)
Keywords
Force feedback,MR fluid,Impulsive force
Submission Author
Taiga Shimizu
Chuo University
Taiki Masuda
Chuo University
Ryunosuke Sawahashi
Chuo University
Manabu Okui
Chuo University
Rie Nishihama
Chuo University
Taro Nakamura
Chuo University

Comment submit