Electrorheological Behavior of Boric Acid Doped Magnetic and Conducting Ni-Ferrite/ Chitosan Biocomposite
ID:75
Submission ID:83 View Protection:ATTENDEE
Updated Time:2023-03-28 10:15:34 Hits:800
Poster Presentation
Abstract
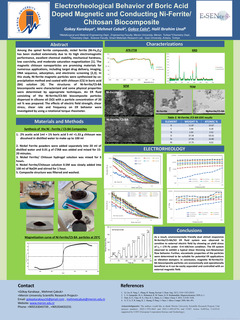
Among the spinel ferrite compounds, nickel ferrite (Ni-Fe2O4) has been studied extensively due to its high electromagnetic performance, excellent chemical stability, mechanical hardness, low coercivity, and moderate saturation magnetization [1]. The magnetic chitosan nanoparticles are promising materials for numerous applications, including target drug delivery, imaging, DNA sequence, adsorption, and electronic screening [2]. Electrorheological (ER) fluids exhibit very important behaviors such as turning into a solid state with the effect of an external electric field strength (E), and returning to a fluid state in a very short time reversibly. ER fluid technology has the potential to be used as an active control system and vibration damping units in various engineering fields such as shock absorbers, valves, sensors, clutches, artificial limb systems and seismographs [3]. In this study, Ni-ferrite magnetic particles were synthesized by co-precipitation method and coated with chitosan (CS) in boric acid (BA) solution [4]. The structures of Ni-ferrite/CS-BA biocomposite were characterized and some physical properties were determined by appropriate techniques. An ER fluid consisting of the Ni-ferrite/CS-BA biocomposite particles dispersed in silicone oil (SO) with a particle concentration of 20 vol % was prepared. The effects of electric field strength, shear stress, shear rate and frequency on ER behavior were investigated by using a rotational torque rheometer.
As a result, environmentally friendly dual stimuli responsive Ni-ferrite/CS-BA/SO ER fluid system was observed to sensitive to external electric field by showing an yield stress of ty = 170 Pa under E=4 kW/mm condition. The ER system observed to exhibit a typical shear thinning non-Newtonian flow behavior. The correlation between the ty and E was deviated from the polarization model (m<2). Further, viscoelastic properties of the particles were determined to be suitable for potential ER applications as vibration dampers. In conclusion, magnetic Ni-ferrite/CS-BA biocomposite particles are economically and operationally beneficial as it can be easily separated and controlled with an external magnetic field.
Keywords
Magnetic chitosan,Ni-ferrite,Electrorheological fluids,Biocomposite
Submission Author
Gokay Karakaya
Mersin University
Mehmet Cabuk
Mersin University
Gokce Calis Ismetoglu
Gazi University
Halil Ibrahim UNAL
Gazi University

Comment submit